Portability of Workflow
Last updated on 2025-06-29 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How can I move my analysis to a computer cluster?
Objectives
- Discuss ways to implement own research directory.
- Explore links to the wider network for computational researchers.
Workflow managers support portability of analysis across compute environments and scale your analysis. This is quite important given the time required to set-up from scratch and work the ropes of using HPC. A good number of HPCs rely on workload managers like Slurm, including the resources I access as a PGR student, at the MVLS school, University of Glasgow. Some the following may map on to the resources you can access to support your research. Please contact your HPC administrator team to request support with setting up.

Once you register an account with your HPC resource, the most straightforward way to install Nextflow is by creating a stand-alone ‘environment’ using the software management tool, conda.
You may require support with this step, please get in touch with your HPC support team. You will also require singularity / apptainer - to set up a container to run your project. Check whether this is already installed, if not please request further support from your HPC team.
Task 13.1
Installing Nextflow is required to run the pipeline. Note this is a different level of abstratction to the auxiliary tools you may are likely to access within your pipeline, i.e docker or apptainer. The more straightforward way to install the Nextflow software and dependencies is to set up a conda environment. Conda or miniforge is commonly made available on compute clusters, as it simplifies downloading software.
conda create --name nf-env bioconda::nextflow
Activate the conda environment.
conda activate nf-env
Install graphviz if you would like to render reports and a timeline for the workflow. May not work if you don’t have elevated permissions, but likely to work on you local machine.
sudo apt install graphviz
Hint: You will need to activate the environment each time you need to use it. You will know you have entered the environment whenever you see the name of the environment appear in parentheses (nf-env) along your command line. The default, i.e no environment is (base).
We saw various different profiles are used to define nextflow configuration profiles to determine how a workflow is actually run on the target system.
If not otherwise specified, processes are run on the local computer. The local runtime is very useful for pipeline development and testing purposes, but for real world computational pipelines an HPC or cloud platform is often required.
You may require support with this step, please get in touch with your HPC support team. You will also require singularity / apptainer - to set up a container to run your project. Check whether this is already installed, if not please request further support from your HPC team.
We can seamlessly transfer analysis from your computer, a grid platform, or the cloud, without modifying it, by simply defining the target platform in the configuration file. This is where our workflow management system shines through and ensures we can build portability and interoperability into our analysis.
Task 13.2
This is specific to SLURM, the workload manager, and involves a batch job submission. Essentially, this command asks for resource for nextflow to schedule a series of jobs and orchestrate the moving parts of our analysis.
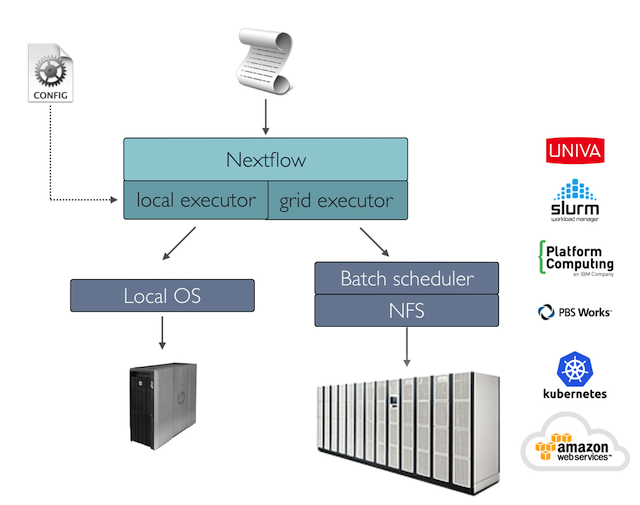
Alas, we can tap into the seamless portability of Nextflow across set
ups (ex. local, slurm, azure). You can switch between these compute
environments by selecting an appropriate profile to run your pipeline.
The appropriate profile in my case was slurm, you can tuck
away this set-up information by creating a new profile in the
conf/ subfolder (ex. conf/slurm.config). Then
the command I would use to schedule the launch of the pipeline say using
2 hours and 5 minutes would involve the following:
BASH
git clone --branch ready-set-workflow --single-branch https://github.com/omiridoue/sgsss-workflow.gitBASH
sbatch -A none -J "demo" --time=02:05:00 --wrap 'nextflow run /mnt/scratch/users/<username>/sgsss-workflow/main.nf -profile slurm'Hint: replace the file path to your sgsss-workflow/main.nf file with the appropriate directory on your computer cluster.
BASH
sacct --starttime 2025-07-10 --format=User,JobID,Jobname%50,partition,state,time,start,end,elapsed,MaxRss,MaxVMSize,nnodes,ncpus,nodelistAn important detail to note is, the time we request to run our batch
job submission is not necessarily the time required to run the entire
pipeline. The reason for this is that sbatch schedules our
jobs to run via nextflow. This means you can max out time permitted to
run your batch submission, to ensure all jobs are submitted within this
time frame. For any jobs submitted within the timeframe but not
scheduled to complete, there is no problem you can prevent a possible
‘time-out’ by specifying
export NXF_DISABLE_JOBS_CANCELLATION=true to add this to
your system variables.
- Nextflow provides an abstraction between the pipeline’s functional logic and the underlying execution system.
- The nextflow configuration file can help define a target platform where we intend to implement our workflow.
- We can specify a profile for our target platform through the
-profileoption.
